________________________________________________________________________________
1106 Perkins - Turbocharger (Inspect and adjust)
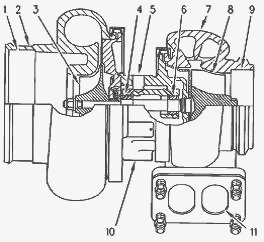
Turbocharger - (1) Air intake (2) Compressor housing (3)
Compressor wheel (4) Bearing (5) Oil inlet port (6) Bearing (7) Turbine
housing (8) Turbine wheel (9) Exhaust outlet (10) Oil outlet port (11)
Exhaust inlet
The turbocharger is mounted on the outlet of the exhaust manifold in one
of two positions on the right side of the engine, toward the top of the
engine or to the side of the diesel engine. The exhaust gas from the
exhaust manifold enters the exhaust inlet (11) and passes through the
turbine housing (7) of the turbocharger. Energy from the exhaust gas
causes the turbine wheel (8) to rotate. The turbine wheel is connected
by a shaft to the compressor wheel (3). As the turbine wheel rotates,
the compressor wheel is rotated. This causes the intake air to be
pressurized through the compressor housing (2) of the turbocharger.
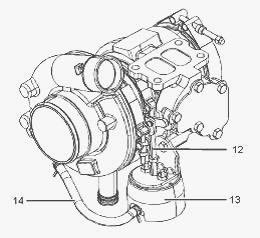
Turbocharger with the waste gate - (12) Actuating lever (13)
Wastegate actuator (14) Line (boost pressure)
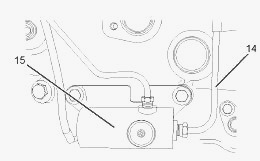
(14) Line (boost pressure) (15) Waste gate solenoid
When the load on the 1106 Perkins engine increases, more fuel is
injected into the cylinders. The combustion of this additional fuel
produces more exhaust gases. The additional exhaust gases cause the
turbine and the compressor wheels of the turbocharger to turn faster. As
the compressor wheel turns faster, air is compressed to a higher
pressure and more air is forced into the cylinders. The increased flow
of air into the cylinders allows the fuel to be burnt with greater
efficiency. This produces more power.
A wastegate is installed on the turbine housing of the turbocharger. The
waste gate is a valve that allows exhaust gas to bypass the turbine
wheel of the turbocharger. The operation of the waste gate is dependent
on the pressurized air (boost pressure) from the turbocharger
compressor. The boost pressure acts on a diaphragm that is spring loaded
in the wastegate actuator which varies the amount of exhaust gas that
flows into the turbine.
If a waste gate solenoid (15) is installed, then the wastegate is
controlled by the engine Electronic Control Module (ECM). The ECM uses
inputs from a number of engine sensors to determine the optimum boost
pressure. This will achieve the best exhaust emissions and fuel
consumption at any given motor operating condition. The ECM controls the
solenoid valve, which regulates the boost pressure to the waste gate
actuator.
When high boost pressure is needed for the motor performance, a signal
is sent from the ECM to the waste gate solenoid. This causes low
pressure in the air inlet pipe (14) to act on the diaphragm within the
wastegate actuator (13). The actuating rod (12) acts upon the actuating
lever to close the valve in the waste gate. When the valve in the
wastegate is closed, more exhaust gas is able to pass over the turbine
wheel. This results in an increase in the speed of the turbocharger.
When low boost pressure is needed for the 1106 Perkins engine
performance, a signal is sent from the ECM to the wastegate solenoid.
This causes high pressure in the air inlet pipe (14) to act on the
diaphragm within the waste gate actuator (13). The actuating rod (12)
acts upon the actuating lever to open the valve inthe wastegate. When
the valve in the wastegate is opened, more exhaust gas from the engine
is able to bypass the turbine wheel, resulting in an decrease in the
speed of the turbocharger.
The shaft that connects the turbine to the compressor wheel rotates in
bearings (4 and 6). The bearings require oil under pressure for
lubrication and cooling. The oil that flows to the lubricating oil inlet
port (5) passes through the center of the turbocharger which retains the
bearings. The oil exits the turbocharger from the lubricating oil outlet
port (10) and returns to the oil pan.
Inspect and adjust
The condition of the turbocharger will have definite effects on engine
performance. Use the following inspections and procedures to determine
the condition of the turbocharger. Inspection of the compressor and the
compressor housing. Inspection of the turbine wheel and the turbine
housing. Inspection of the wastegate.
Inspection of the Compressor and the Compressor Housing - Inspect the
compressor wheel for damage from a foreign object. If there is damage,
determine the source of the foreign object. Replace the turbocharger.
Turn the rotating assembly by hand. While you turn the assembly, push
the assembly sideways. The assembly should turn freely. The compressor
wheel should not rub the compressor housing.
The turbocharger must be replaced if the compressor wheel rubs the
compressor wheel housing. Inspect the compressor and the compressor
wheel housing for oil leakage. An oil leak from the compressor may
deposit oil in the aftercooler. If oil is found in the aftercooler, then
drain and clean the aftercooler.
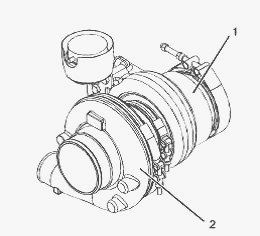
(1) Turbine housing (2) Compressor housing
Check the oil level in the crankcase. If the oil level is too high,
adjust the oil level. Inspect the engine crankcase breather. Clean the
1106 Perkins engine crankcase breather or replace the engine crankcase
breather if the engine crankcase breather is plugged. Remove the pipe
for the oil drain. Inspect the drain opening. Inspect the oil drain
line. Inspect the area between the bearings of the rotating assembly
shaft. Look for oil sludge. Inspect the oil drain hole for oil sludge.
Inspect the oil drain line for oil sludge in the drain line. If
necessary, clean the oil drain line.
Inspection of the Turbine Wheel and the Turbine Housing - Remove the air
piping from the turbine housing. Inspect the turbine for damage by a
foreign object. If there is damage, determine the source of the foreign
object. Replace turbocharger (2). Inspect the turbine wheel for the
carbon and other foreign material. Inspect turbine housing (1) for
carbon and foreign material. Replace the turbocharger, if necessary.
Turn the rotating assembly by hand. While you turn the assembly, push
the assembly sideways. The assembly should turn freely. The turbine
wheel should not rub turbine wheel housing (1). Replace turbocharger (2)
if turbine wheel rubs turbine housing (1). Inspect the turbine and
turbine housing (1) for oil leakage. Inspect the turbine and turbine
housing (1) for oil coking. Some oil coking may be cleaned. Heavy oil
coking may require replacement of the turbocharger.
Remove the pipe for the oil drain. Inspect the drain opening. Inspect
the area between the bearings of the rotating assembly shaft. Look for
oil sludge. Inspect the oil drain hole for oil sludge. Inspect the oil
drain line for oil sludge. If necessary, clean the drain line. If
crankcase pressure is high, or if the oil drain is restricted, pressure
in the center housing may be greater than the pressure of turbine
housing (1). Oil flow may be forced in the wrong direction and the oil
may not drain. Check the crankcase pressure and correct any problems. If
the oil drain line is damaged, replace the oil drain line. Check the
routing of the oil drain line. Eliminate any sharp restrictive bends.
Make sure that the oil drain line is not too close to the engine exhaust
manifold.
Inspection of the Wastegate - The wastegate controls the amount of
exhaust gas that is allowed to bypass the turbine side of the
turbocharger. This valve then controls the rpm of the turbocharger. When
the engine operates in conditions of low boost (lug), a spring presses
against a diaphragm in the canister. The actuating rod will move and the
wastegate actuator will close. The turbocharger can then operate at
maximum performance.
When the boost pressure increases against the diaphragm in the canister,
the wastegate will open. The rpm of the turbocharger becomes limited.
The rpm limitation occurs because a portion of the exhaust gases bypass
the turbine wheel of the turbocharger. The following levels of boost
pressure indicate a problem with the wastegate: Too high at full load
conditions / Too low at all lug conditions.
The boost pressure controls the maximum rpm of the turbocharger, because
the boost pressure controls the position of the wastegate. The following
factors also affect the maximum rpm of the turbocharger: The 1106
Perkins engine rating, The horsepower demand on the engine, The high
idle rpm, Inlet air restriction, Exhaust system restriction.
Check the Wastegate for Proper - Disconnect the pipe for the boost
sensor (7) at the wastegate actuator (6). Connect an air supply to the
wastegate actuator that can be adjusted accurately. Install Tooling to
the turbocharger so that the end of the actuator rod (4) is in contact
with Tooling (A). This will measure axial movement of the actuator rod
(4).
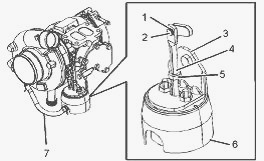
Slowly apply air pressure to the wastegate so that the actuator rod (4)
moves 1.0 mm (0.039 inch). Ensure that the dial indicator returns to
zero when the air pressure is released. Repeat the test several times.
This will ensure that an accurate reading is obtained. If the operation
of the wastegate is not correct, the actuator rod (4) can be adjusted.
Remove Tooling from the turbocharger.
When the air pressure is applied, loosen the nut (5) on the actuator.
Remove the circlip (1). Remove the pin (2) from the actuator rod (4).
When the air pressure is too low, adjust the end of the actuator rod (4)
in order to reduce the length of the actuator rod (4). If the air
pressure is too high, adjust the end of the actuator rod (4) in order to
increase the length of the actuator rod (4). Install the pin (2) to the
actuator rod (4). Install the circlip (1) to the actuator rod (4).
Tighten the nut (5) to a torque of 5 Nm (44 lb in). If the air pressure
is correct, remove the air supply. Remove Tooling. Install the pipe for
the boost sensor (7).
________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________

 SPECS
SPECS LOADERS
LOADERS MAINTENANCE
MAINTENANCE PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS MF 1523
MF 1523 MF 1531
MF 1531 MF 135
MF 135 MF 1547
MF 1547 MF 1635
MF 1635 231
231 231S
231S 235
235 240
240 241
241 255
255 265
265 274
274 285
285 375
375 916X Loader
916X Loader 921X Loader
921X Loader 926X Loader
926X Loader 931X Loader
931X Loader 936X Loader
936X Loader 941X Loader
941X Loader 946X Loader
946X Loader 951X Loader
951X Loader 956X Loader
956X Loader 988 Loader
988 Loader 1655
1655 GS1705
GS1705 1742
1742 2635
2635 4608
4608 1080
1080 1100
1100 2615
2615 3050
3050 3060
3060 4708
4708 5455
5455 5450
5450 5610
5610 5613
5613 DL95 Loader
DL95 Loader DL100 Loader
DL100 Loader DL120 Loader
DL120 Loader DL125 Loader
DL125 Loader DL130 Loader
DL130 Loader DL135 Loader
DL135 Loader DL250 Loader
DL250 Loader DL260 Loader
DL260 Loader L90 Loader
L90 Loader L100 Loader
L100 Loader 6499
6499 7480
7480 7618
7618 7726
7726 1533
1533 2604H
2604H 2607H
2607H 4455
4455 4610M
4610M 4710
4710 L105E Loader
L105E Loader L210 Loader
L210 Loader 1014 Loader
1014 Loader 1016 Loader
1016 Loader 1462 Loader
1462 Loader 1525 Loader
1525 Loader 1530 Loader
1530 Loader 232 Loader
232 Loader 838 Loader
838 Loader 848 Loader
848 Loader 5712SL
5712SL 6713
6713 6715S
6715S 7475
7475 7615
7615 7716
7716 7724
7724 8240
8240 8650
8650 8732
8732 246 Loader
246 Loader 1036 Loader
1036 Loader 1038 Loader
1038 Loader 1080 Loader
1080 Loader 856 Loader
856 Loader